Diving into the intricate relationship between gut health and brain function, this introduction sets the stage for a fascinating journey into how our gut impacts our cognitive abilities and mental well-being. From the significance of gut health to the fascinating gut-brain axis, get ready to unravel the mysteries of this crucial connection.
As we delve deeper, we will uncover the profound impact of gut health on brain function and explore strategies to enhance both aspects for a healthier mind and body.
Gut Health Overview
Having a healthy gut is crucial for overall well-being as it plays a significant role in various bodily functions. One key component of gut health is the gut microbiome, a diverse community of bacteria, fungi, and other microorganisms that reside in the intestines.
The Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome is essential for maintaining a healthy gut as it helps with digestion, nutrient absorption, and even immune function. A balanced and diverse gut microbiome is associated with better overall health and can help prevent various digestive issues and diseases.
Factors Influencing Gut Health
- Diet: What you eat directly impacts the health of your gut. A diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables can promote a healthy gut microbiome, while a diet high in processed foods and sugars can negatively affect gut health.
- Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of bacteria in the gut and lead to inflammation, affecting overall gut health.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as antibiotics, can alter the gut microbiome by killing off beneficial bacteria, which can have a negative impact on gut health.
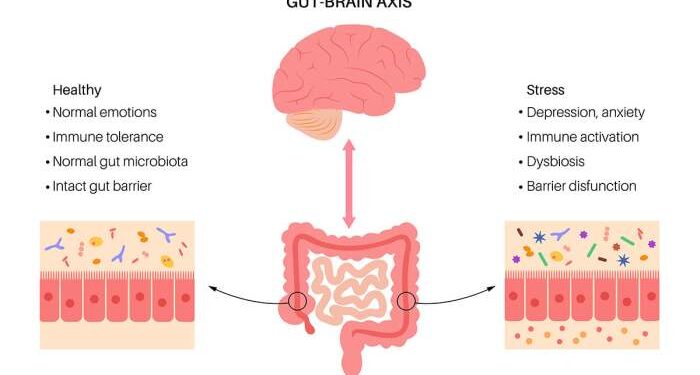
Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system that connects the gut and the brain, allowing them to influence each other's function and health. This complex network involves various pathways through which the gut microbiome can communicate with the brain and vice versa.
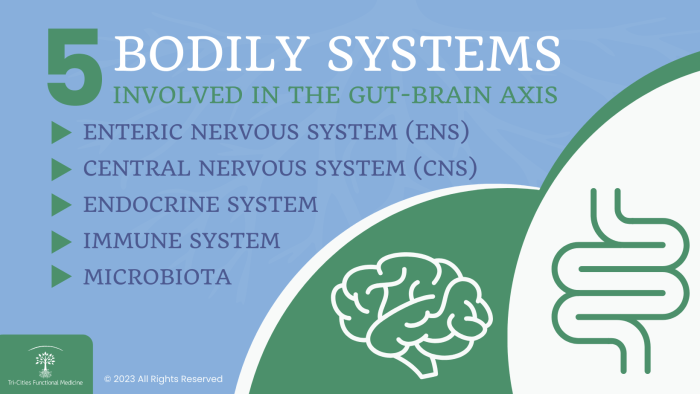
Communication Pathways
The gut and the brain communicate through multiple pathways, including the nervous system, the immune system, and the endocrine system. The vagus nerve, which runs from the brain to the gut, plays a crucial role in this communication by transmitting signals in both directions.
Additionally, the gut microbiome produces neurotransmitters and metabolites that can affect brain function and behavior.
Influence of Gut Microbiome on Brain Function
The gut microbiome, composed of trillions of bacteria living in the gastrointestinal tract, plays a significant role in influencing brain function. These bacteria produce neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for regulating mood and behavior. Moreover, the gut microbiome can modulate inflammation and immune responses, which have been linked to conditions such as depression and anxiety.
Impact of Brain on Gut Microbiome
Conversely, the brain can also influence the composition and function of the gut microbiome. Stress, for example, can alter the balance of gut bacteria and increase gut permeability, leading to inflammation and gastrointestinal problems. This highlights the intricate relationship between gut health and brain function, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiome for overall well-being.
Impact of Gut Health on Brain Function
Poor gut health can have a significant impact on cognitive functions and overall brain health. The gut-brain axis plays a crucial role in regulating mood, behavior, and cognitive processes.
Effect on Cognitive Functions
- Impaired memory and concentration
- Reduced ability to learn new information
- Slower processing speed
Relationship with Mental Health Conditions
There is a strong connection between gut health and mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. An unhealthy gut can lead to inflammation, which in turn affects mood regulation and emotional well-being.
Potential Link with Neurological Disorders
- Alzheimer's disease
- Parkinson's disease
- Multiple sclerosis
Strategies to Improve Gut Health for Better Brain Function
Improving gut health can have a significant impact on brain function. By making simple dietary and lifestyle changes, you can promote a healthy gut microbiome and enhance cognitive function.
Dietary Changes for a Healthy Gut Microbiome
One of the most effective ways to improve gut health is by incorporating more fiber-rich foods into your diet. Fiber helps feed the good bacteria in your gut, promoting a diverse microbiome. Foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes are great sources of fiber.
- Include fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi in your diet. These foods contain beneficial probiotics that can help balance your gut flora.
- Avoid processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-fat meals, as these can negatively impact gut health and promote inflammation.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day. Hydration is essential for proper digestion and overall gut health.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Gut Health and Brain Function
In addition to dietary changes, certain lifestyle modifications can also promote a healthy gut and improve brain function.
- Manage stress through practices like yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, or spending time in nature. Chronic stress can disrupt the gut-brain axis and impact cognitive function.
- Get regular exercise to support a healthy gut microbiome. Physical activity can help regulate bowel movements and promote a diverse range of gut bacteria.
- Ensure an adequate amount of sleep each night. Poor sleep can disrupt the gut microbiome and affect cognitive processes.
Probiotic and Prebiotic Foods to Enhance Gut Health
Probiotics and prebiotics are beneficial for gut health as they help maintain a balanced microbiome.
- Probiotic foods include yogurt, kefir, kombucha, miso, and pickles. These foods contain live beneficial bacteria that can help improve gut health.
- Prebiotic foods like garlic, onions, bananas, asparagus, and oats provide fiber that nourishes the good bacteria in your gut.
- Consider taking a high-quality probiotic supplement if you have trouble incorporating enough probiotic-rich foods into your diet.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the intricate interplay between gut health and brain function underscores the importance of maintaining a healthy gut for optimal cognitive and mental health. By understanding and nurturing this connection, we pave the way for a brighter, sharper mind and a happier, healthier life.
FAQ Explained
How does gut health influence brain function?
Gut health impacts brain function through the gut-brain axis, where the gut microbiome communicates with the brain, affecting cognitive abilities and mental well-being.
Can poor gut health lead to neurological disorders?
There is a potential link between poor gut health and neurological disorders, as an unhealthy gut can contribute to inflammation and other factors that may affect brain health.
What are some dietary changes to promote a healthy gut microbiome?
Consuming fiber-rich foods, fermented foods, and foods high in probiotics can help promote a healthy gut microbiome, which in turn benefits brain function.